Introduction
We often think about sleep in such a way that when our body is completely tired and we are just lying down to rest, our body shuts down and our mind is at a different stage during this sleep, that is, at a different quality. It happens and our health depends largely on this, which is where the human brain is processing its memory.Understanding these sleep stages can help you improve the quality of your rest and, in turn, your daily performance and long-term health.
What Are Sleep Stages?
Sleep is not the same experience every time. Some types of sleep are of two typesNon-REM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) sleep and REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep. These two types alternate in cycles throughout the night,This sleep cycle lasts for about ninety minutes and each cycle has a different characteristic and each cycle has a different importance during which our body recovers and makes it healthy. It helpswith each cycle lasting about 90 minutes. Each stage of sleep within these cycles has distinct functions that are crucial for both mental and physical health.
Let’s break down the stages of sleep with me and try to understand each stage better
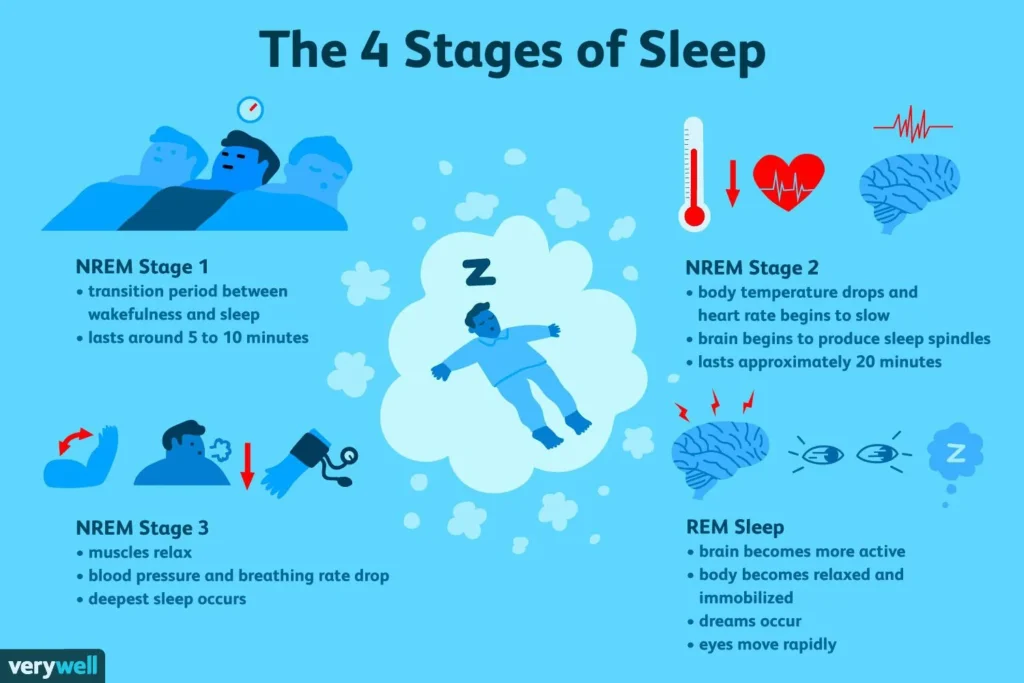
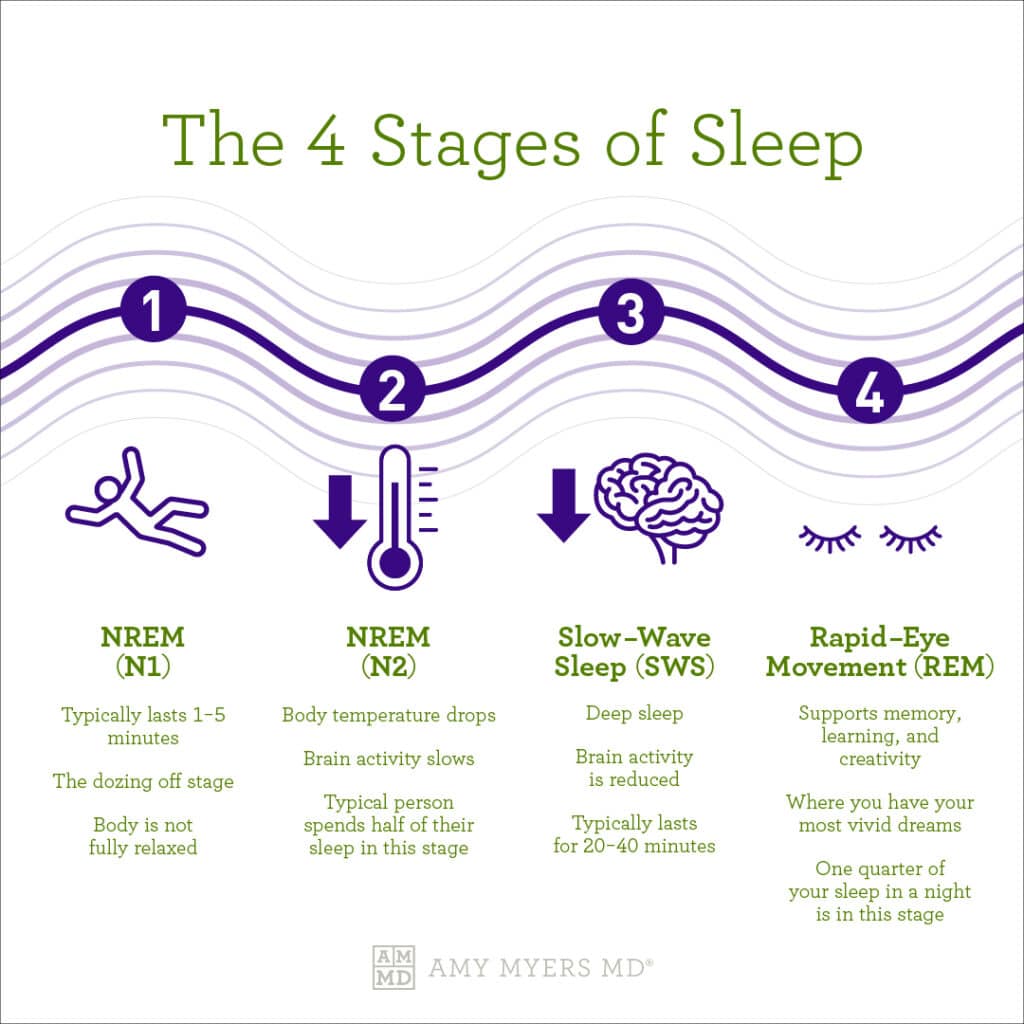
Stage 1: Light Sleep (Non-REM)
The first stage of sleep is a light sleep, lasting only a few minutes. During this stage:
- Your body starts to relax.
- Your brain slows down, but you’re still somewhat aware of your surroundings.
- Your breathing becomes more regular, and your heart rate starts to slow.
Well, this is the part between sleep and wakefulness. Within this part, the person is going into sleep and gradually moving towards deep sleep.

Stage 2: Deeper Light Sleep (Non-REM)
Although it is a little deeper than stage 1, stage 2 is still regarded as light sleep. This 20-minute stage makes for around half of your whole sleep duration. In phase two:
- Your body temperature drops.
- Your muscles relax even further.
- The brain starts to slow down as sleep begins, with sporadic spikes known as “sleep spindles” that help shield the slumber from outside distractions.
This phase is essential for getting your body ready to go into the more restorative, deeper sleep stages.

Stage 3: Deep Sleep (Non-REM)
Your body needs to go through this phase in order to be ready to go into the deeper, more restorative sleep phases.
- Blood pressure drops.
- Breathing becomes slower and more regular.
- Tissue growth and repair take place.
- The immune system strengthens.
For the body to heal physically, to build muscle, and to strengthen the immune system, deep sleep is necessary. Toxin removal from the brain is also crucial, as this may aid in the prevention of neurodegenerative illnesses like Alzheimer’s. Even after what appears to be a full night of sleep, people who don’t obtain enough deep sleep may wake up feeling exhausted.
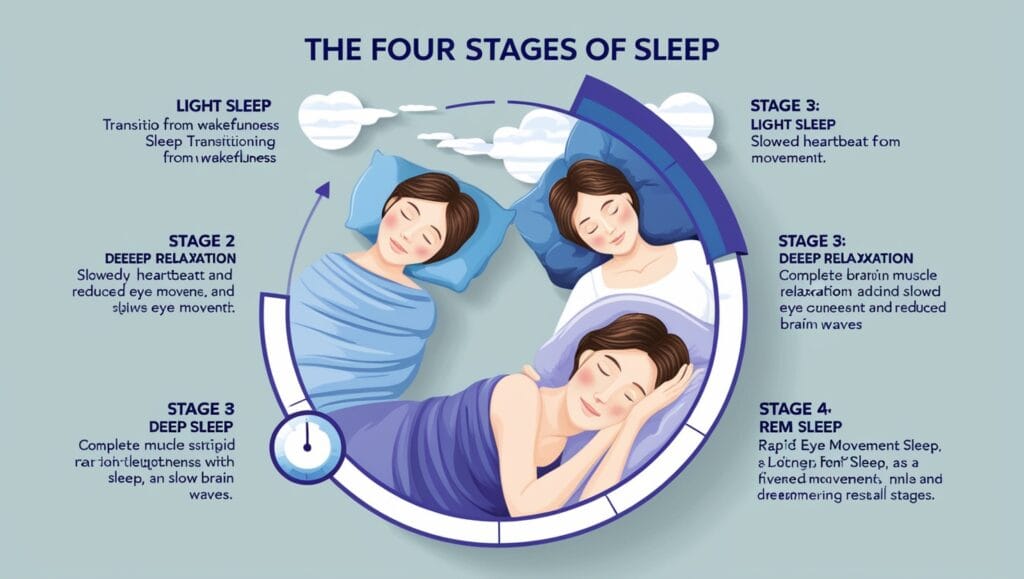
Stage 4: REM Sleep
Your body enters REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, which is most closely linked to dreaming, after passing through the three stages of non-REM sleep. This phase intrigues me because to:
- Your brain starts functioning at its peak when you’re asleep.
- The name comes from the quick movement of your eyeballs behind your eyelids.
- Your respiration and heart rate quicken.
- Your muscles go into a temporary paralysis so that you can’t live out your dreams.
Memory consolidation, emotional processing, and mental renewal all depend on REM sleep. It’s the process by which your brain processes the events of the day, storing the crucial knowledge in memory and eliminating the unimportant. During the night, REM sleep typically begins 90 minutes after falling asleep and gets longer with each cycle.